Deep Caries
Deep caries usually develop between two adjacent teeth. Here they are protected from the toothbrush and can only be stopped in the early stages by dental floss. Dentists can detect these caries at an early stage using special X-ray images. If the bacteria reach deeper layers over a longer period of time, this requires special measures to preserve the tooth.
- Gentle, painless and modern treatment methods
- Early detection and prevention concept
- Minimally invasive treatment and high-quality fillings
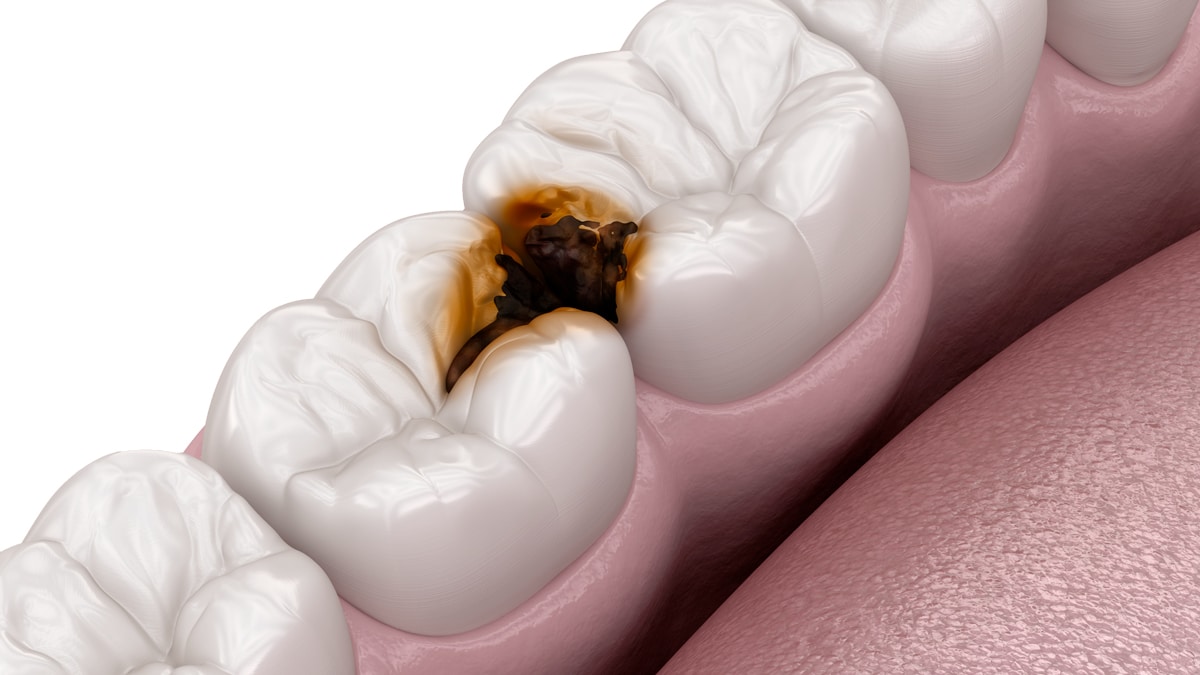
What is deep caries?
The tooth has two different layers. If the caries has broken through both layers, it is called deep caries. Teeth that are suddenly sensitive to cold can indicate this.
The dentist calls deep caries: caries profunda. This term defines a certain stage or depth of caries.
The end result of untreated caries is the death of the pulp. The pulp is also commonly referred to as the nerve.
However, before the bacteria reach the nerve, they have to eat their way through various layers in the tooth. To do this, the bacteria convert sugar into acid. The acid slowly destroys the hard substances of the tooth and a deep hole is created.
The closer the caries comes to the nerve, the more likely it is that severe toothache will occur as a symptom.
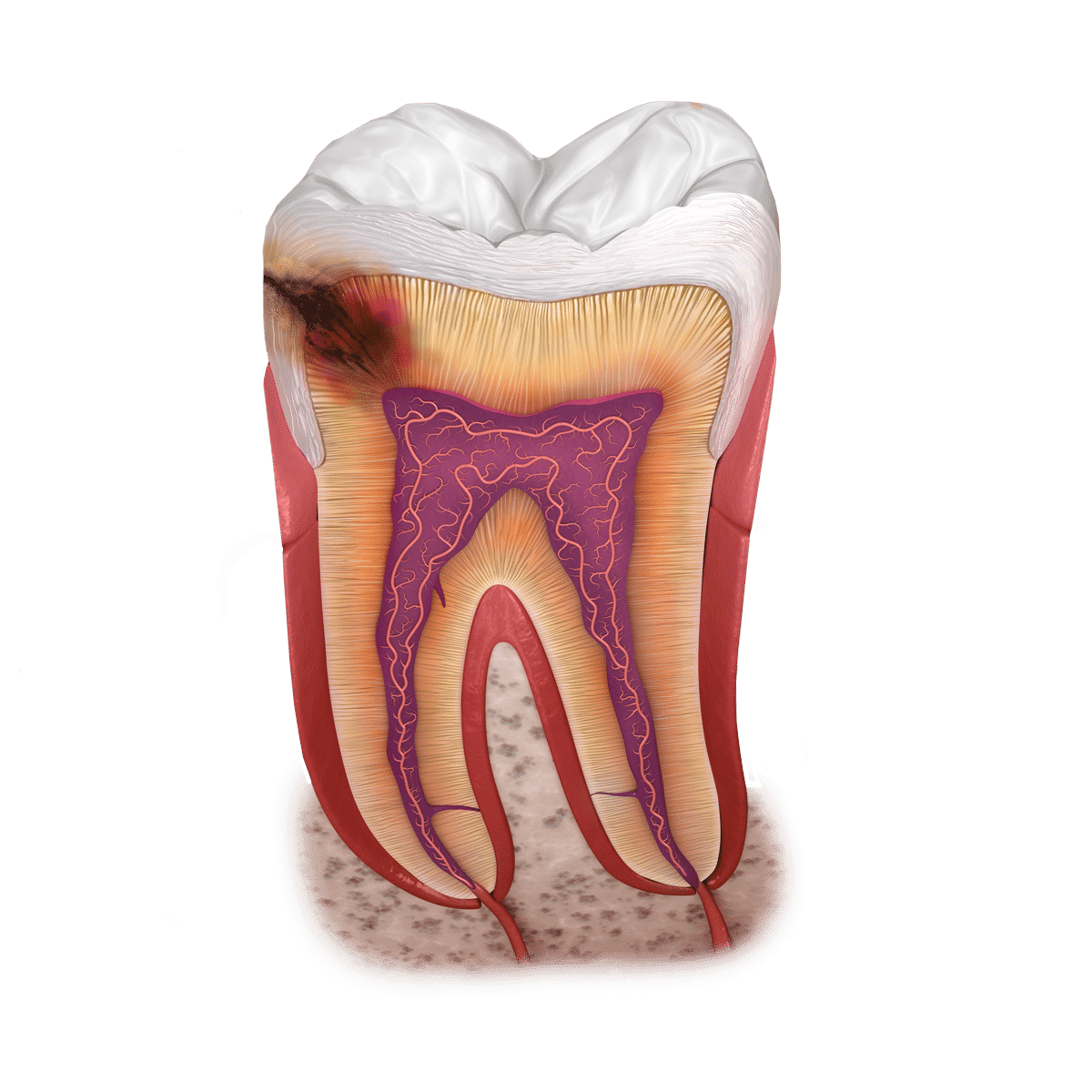
Bacteria eat a deep hole in the layers of the tooth. Sugar is the staple food for the bacteria. A small entrance is enough to attack the soft interior of the tooth.
The inner dentin is softer and can be decomposed particularly quickly by bacteria. The distance to the inner nerve is not far.
The dental pulp, also known as the pulp. The pulp is the soft interior of the tooth, which contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue.
Once the bacteria have reached the inner nerve of the tooth, the greatest pain occurs and the tooth dies. Preserving such a tooth is a health risk.
Find out more about our practice in our patient interviews
Gentle caries treatment with DR. HAGER
Do you have tooth decay, bad teeth or a cavity? We treat caries painlessly and minimally invasively.
At our dental practice in Bietingen and dental practice in Constance, we use the gentlest, most painless and modern dental procedures possible, high-quality fillings and minimally invasive dentistry to diagnose and treat tooth decay.

Tooth enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth and consists of mineralized cells. It is the hardest component of the human body.
Inside the tooth (pulp) there is healthy blood and nerve tissue, which serve as an important source of life for the tooth. In the case of caries, bacteria can penetrate deep inside. The tooth is then considered infected and usually has to be removed. Other therapies often only prolong the suffering.
The jawbone forms the structure in which the teeth are anchored.
The layers of the tooth
Tooth enamel is the hardest layer of the tooth. It covers the entire visible outer surface and is visible to everyone when you smile. Shiny crystal white when well cared for. It protects the tooth from a wide range of irritants that occur in the oral cavity.
Underneath is the much softer dentin. It is browner in color and has small channels that extend to the tooth nerve. These connections make the tooth sensitive and cause pain if they are exposed. Below the dentin is the pulp, which contains blood vessels, tissue and nerves.
Conclusion: Caries spots that overcome the enamel and reach deep layers of the dentin just before the pulp are called caries profunda.
How does tooth decay develop?
Caries is caused by plaque: a white, sticky biofilm that forms on the surface of the teeth. This tough substance contains bacteria and nutrients.
The bacterium Streptococcus mutans is the most damaging. However, before the affected areas in the mouth become pathogenic, i.e. harmful, this biofilm has to sort itself into special layers on the tooth over a period of 24 hours.
If you now remove this plaque regularly by brushing, no caries can form. The biofilm does not necessarily have to be removed 100%. It is sufficient to comb through it, disrupting the bacterial structure.
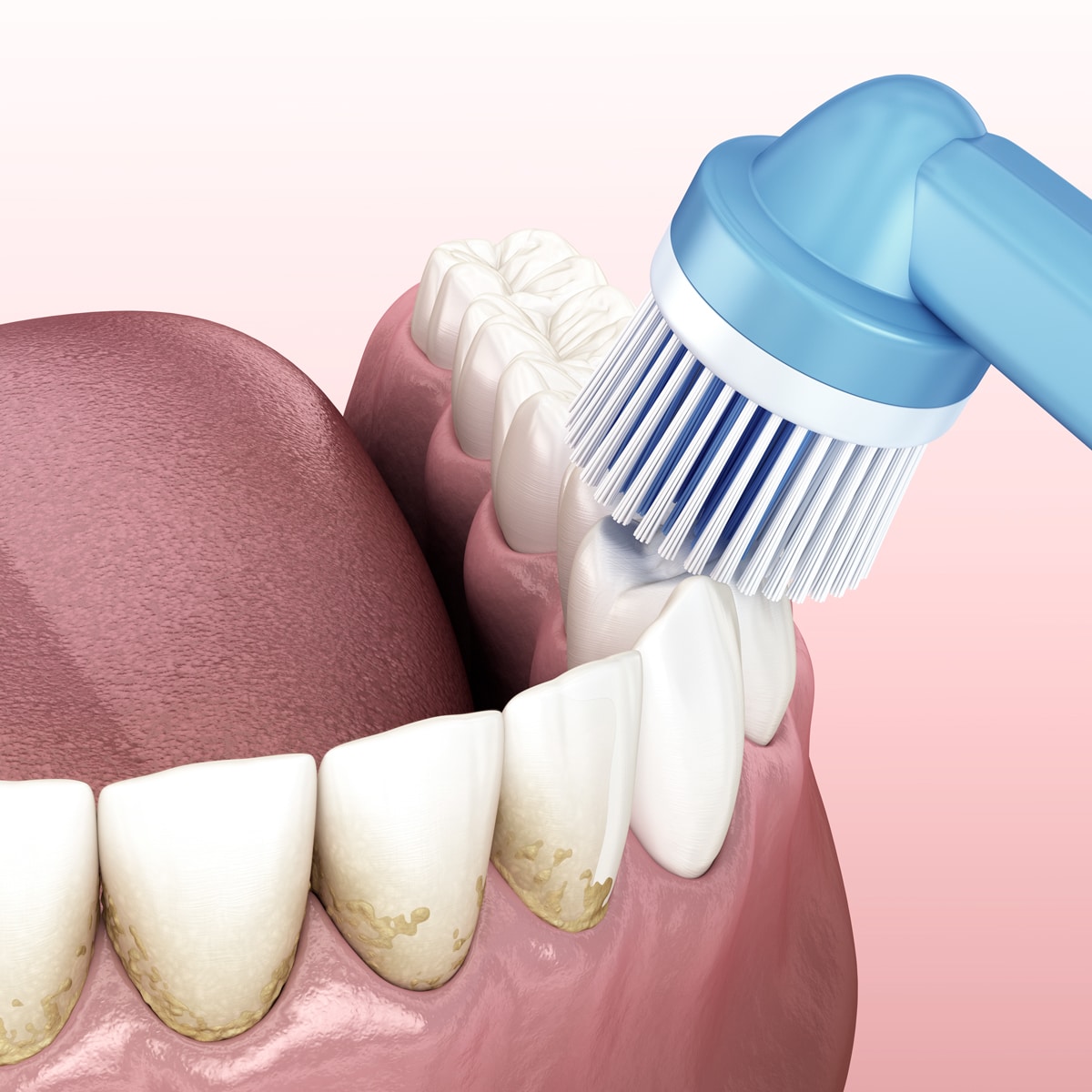
For optimal dental care, we recommend not only using the ultrasonic toothbrushes, but also the small interdental brushes between the teeth, as this is where caries usually develops.
Poor dental care leads to the accumulation of plaque and tartar, which increases the risk of tooth decay.
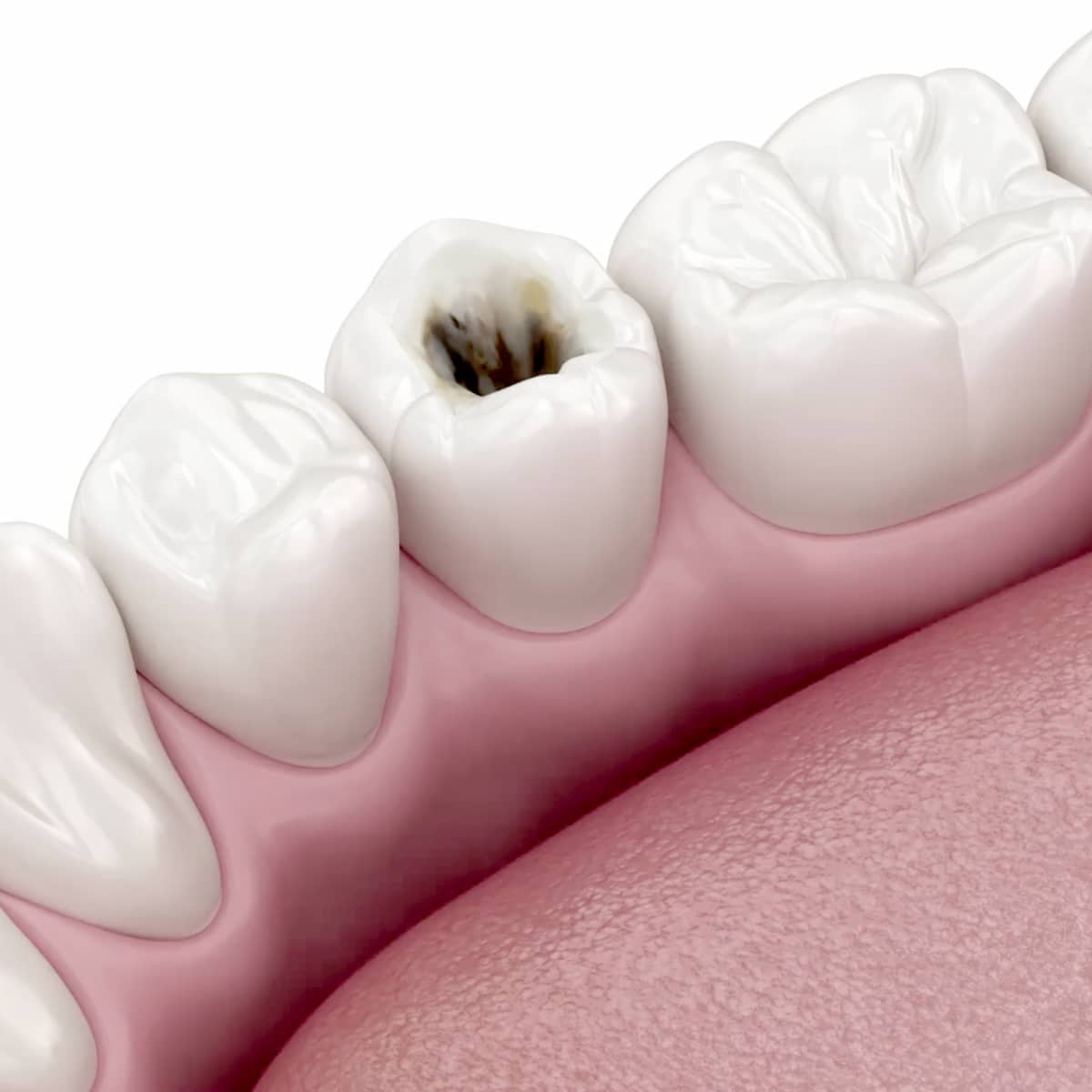
Deep caries is an advanced stage of dental caries in which the damage to the tooth penetrates into the deep layers, including the pulp.
Caries causes holes
Once the pathogenic bacterial structure has built up over 24 hours, the bacteria can finally form organic acids from sugar. In this case, the acids are the cause of the loss of substance in the enamel and thus the cavity.
The hole in the enamel now serves as additional protection for the caries and must be treated by the dentist before the tooth nerve is reached.
After the caries has been removed, the hole is sealed bacteria-proof with a filling. This is best done with a ceramic inlay.
Caries and X-rays
First, carious areas must be can be reliably recognized. White and brownish spots or even defects on exposed surfaces are visible to the naked eye and indicate possible caries.
Inflammation of the gums and exposed carious edges of fillings or crowns are also reliably detected by the dentist. However, the visible surfaces are cleaned by the patient anyway during thorough oral hygiene
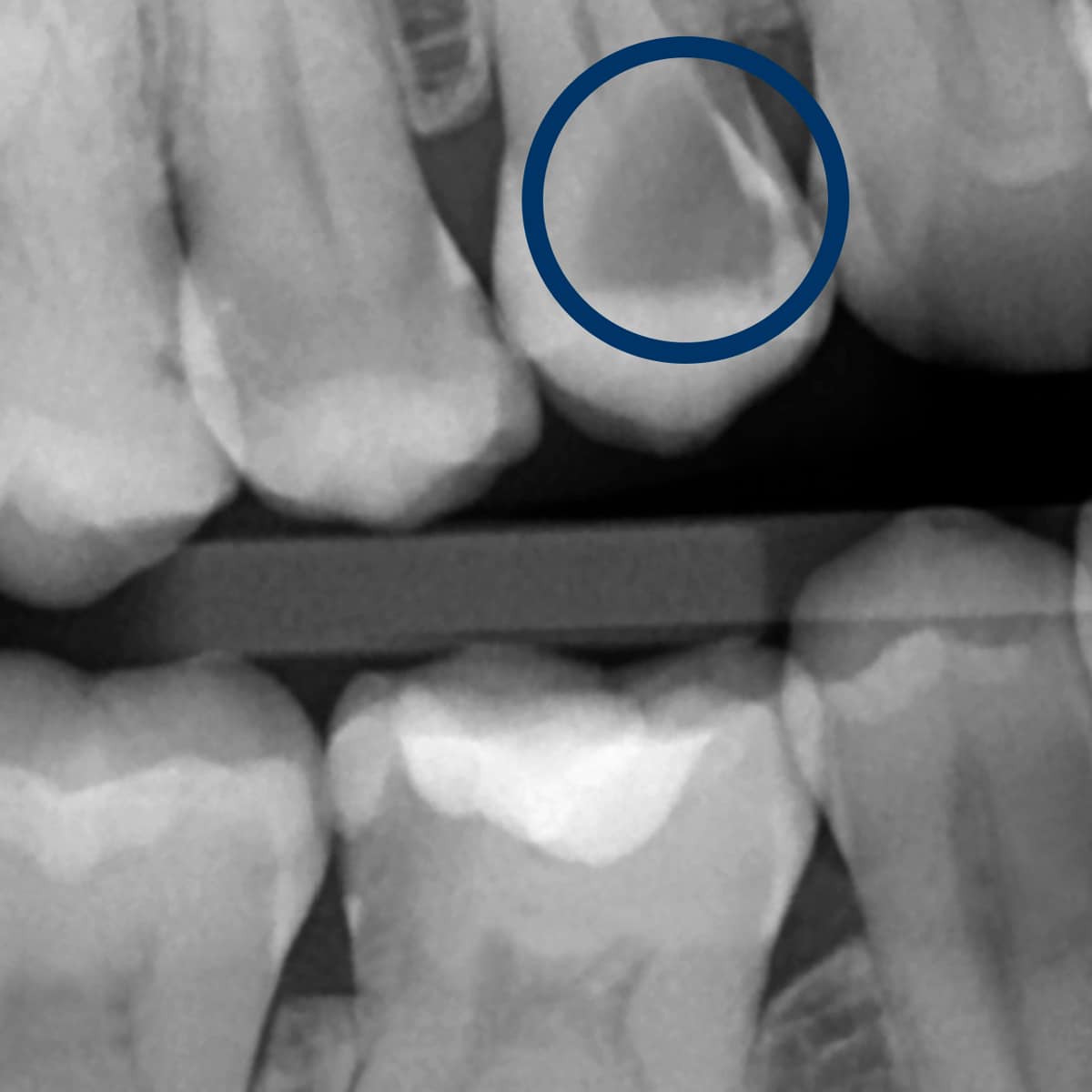
View of a deep caries on an X-ray image
Here you can see a (secondary) caries. This is a caries on an existing filling. This usually occurs on plastic fillings. Plastic fillings are a material that is not permanently impermeable and so bacteria can re-enter after a while.
Treatment of deep caries

Detection of deep caries in dental check-ups
First of all, carious areas must be reliably identified. White and brownish spots or even defects on exposed surfaces are visible to the naked eye and indicate possible caries.
Inflammation of the gums and exposed carious edges of fillings or crowns are also reliably detected by the dentist. However, the visible surfaces are cleaned by the patient anyway during thorough oral hygiene.
The interdental spaces are much more difficult to clean and therefore more at risk, which the dentist can only visualize reliably with x-rays.
When does a caries need to be treated?
If caries is detected, it must be treated depending on its severity. Mild demineralization can even be reversed with good care and fluoride preparations. However, if it extends beyond the enamel into the dentin, it is not reversible and must be treated by a dentist.
Symptoms such as spontaneous pain or sensitivity to cold on the affected tooth can signal that caries is already well advanced. Based on the X-ray image and the clinical picture, the dentist will now make a diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment.

How does the dentist remove caries?
In the case of deep caries treatment, access and an overview of the caries must first be created. Special slow-rotating rose burs remove the softened, infected substance from the tooth. This is done very carefully so as not to open the tooth nerve unnecessarily.
On the other hand, it is extremely important to remove any caries from the tooth. If the tooth nerve is opened up by caries that is too deep, an inflammation of the pulp can usually be observed, which manifests itself in heavy bleeding.
If the bleeding can be stopped, the pulp can be sealed with special preparations. The resulting hole is then sealed with a temporary but very dense cement. We now wait 3 months to ensure that the tooth will survive in the long term. Only then can a decision be made about further treatment.
The definitive solution after a deep caries.
Surprisingly, the dental nerve walls up the hole in the nerve from the inside again if your body provides sufficient resistance. If the dental nerve is still vital after several months, a definitive restoration can be planned and carried out.
The special seal of the pulp is ideally left in place or renewed when the cavity is reopened. Now we give the remaining tooth a special resistant polish. The resulting tooth shape is then digitally scanned using a 3D scanner and a precisely fitting ceramic inlay can be inserted in a subsequent appointment.
Filling variants and their advantages disadvantages
If deep caries is not detected or removed, there is a risk of tooth loss. At an early stage, the dentist can reliably heal the affected tooth by removing the caries with a drill and sealing it with a filling.
Special treatment is required for late stages.
Areas close to the nerve are treated and covered with special materials and medication. A conventional filling is then used on top.

1. The ceramic inlay as the highest quality filling: stable, dense, beautiful. An invention from Switzerland, white & naturally modeled in 3D, just as nature intended.
2. The gold inlay: very durable, dense, risk of fracture of the tooth substance, not beautiful.

3. Amalgam fillings are considered to be very dense, but unfortunately have disadvantages in terms of compatibility and esthetics, as well as susceptibility to fracture.
4. The composite filling: for the anterior region. However, it has clear deficiencies in the posterior region.

“For me, ceramic inlays are the optimal filling option for posterior teeth. The high masticatory forces are reliably absorbed and an unrivaled marginal integrity enables impressive longevity. With good oral hygiene, it will last a lifetime, just like your intact teeth.
Dr. Eva Krapf
A tooth dies, what should I do?
If the dental nerve dies, follow-up treatment must be carried out. After a short time, the nerve canal is colonized by bacteria, which can cause severe toothache.
Many dentists now carry out root canal treatment, which in the best case completely fills the main canal. However, the side canals and numerous porosities always remain colonized by bacteria.
As numerous studies have shown, it is only possible to achieve a reduction in germs with files and rinsing solutions. The remaining and constantly multiplying bacteria must then be kept in check by the body’s defense systems for years.
However, the constant bacterial load cannot be removed from the patient in this way. Bacteria that enter the bloodstream from these so-called foci (bacteremia) can promote many chronic secondary diseases.
For these reasons, we recommend that our patients remove these teeth before further treatment, because health has priority. We therefore generally advise against root canal treatment for the reasons mentioned above.
For this reason, our top priority is to try to preserve the dental nerve by all means possible. This is because a tooth with a regenerated nerve will keep the canal sterile on its own and is thus completely repaired.
However, if this is not possible, the tooth is replaced with a bridge or an implant. This restores the sterility of the surrounding tissue.

Avoid tooth decay
- Preventing tooth decay in advance requires good dental care at home with professional guidance and training. Ideally, children should already be sensitized and introduced to thorough oral hygiene through dental check-ups and dental hygiene sessions.
- A child with good oral hygiene will carry this into adulthood, drastically increasing their chances of lifelong dental health.
- We recommend thorough dental care with a toothbrush and interdental brushes.
- Regular professional dental cleanings should always be carried out to support this. This improves the brushing technique and cleans and polishes hard-to-reach niches. Tartar and incipient gum inflammation are reliably detected and treated.

We look forward to seeing you!
If you have any questions or would like advice on optimal dental care, we will be happy to help you personally. Visit us during our consultation hours at one of our two dental practices in Germany.
and the entire Dr Hager team

Frequently asked questions about deep caries
How do I recognize caries or deep caries?
Carious spots are difficult to detect as they mainly occur in places that are not visible. Even if you discover brownish spots, this is not necessarily caries. Spontaneous toothache can be an indicator of advanced tooth decay. However, there are many other causes that could cause this pain. A clear diagnosis can only be made by a dentist.
Why does tooth decay cause pain?
As the protective layer of the tooth has been broken through, stimuli can be conducted through small dentinal tubules to the pulp. Stimuli include cold and heat. However, chemical and mechanical stimuli can also trigger pain.
Do fillings or crowns protect the tooth from new bacterial infestation?
No, damage to the filling and crown margins can occur again due to inadequate oral hygiene. However, direct damage to the filling material caused by microorganisms is ruled out.
Where do caries form most frequently?
Between the teeth, as only special cleaning agents clean effectively here. For example, dental floss or, better, interdental brushes.
Which type of filling do you recommend for anterior and posterior teeth?
We recommend metal-free ceramic inlays for posterior teeth. These can withstand the high chewing forces and do not change their shape. This means that a lifelong seal can be achieved. We recommend composites for anterior teeth. Composites are suitable for smaller volumes and lower masticatory forces. They also achieve good esthetics.