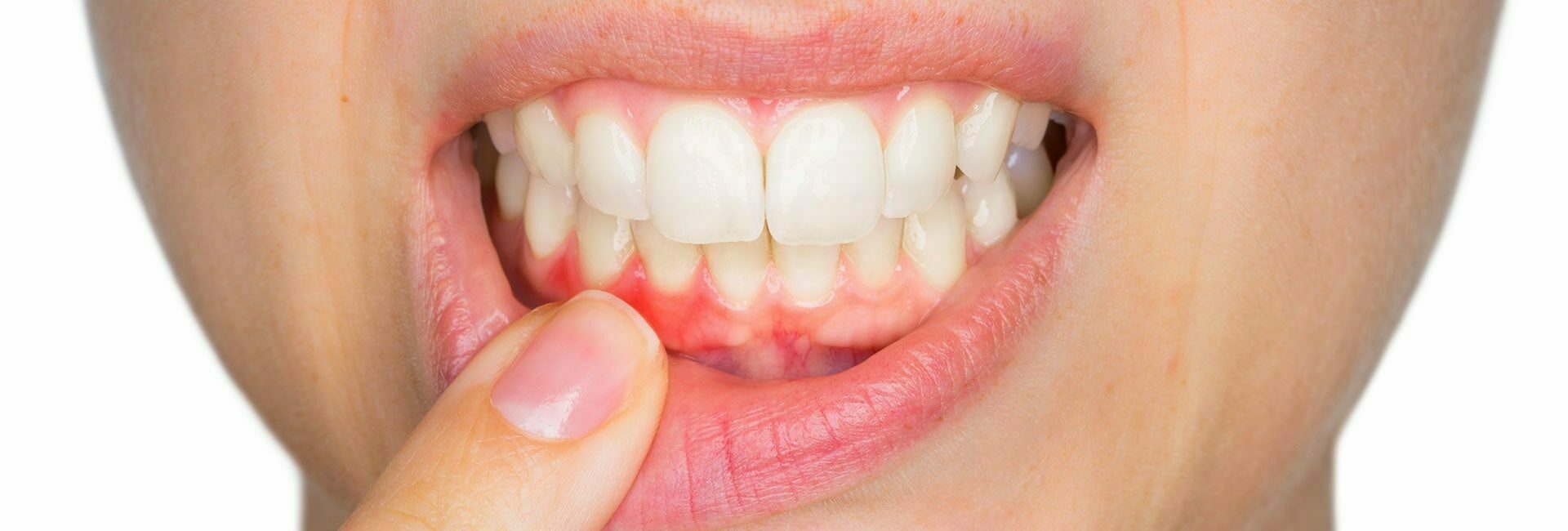
Inflammation of the gums: are bleeding gums a disease?
The function of the gums is to cover the jaw bone and to create a tight, collar-like seal around all of the teeth set in it. No bacteria should be allowed to enter between the gums and the teeth. If patients don’t remove bacteria which accumulates on the gums at regular intervals, by using toothbrushes, floss, or interdental brushes, then they may suffer from the symptoms of acute inflammation of the gums (acute gingivitis). Colonies of bacteria attack the gums and break it down.
The body responds to this attack with an inflammatory reaction produced by the bloodstream: the gums swell up, turn a darker red colour, and when these gums are just slightly irritated, bleeding occurs. This is when a dentist will start to refer to a case of gingivitis. Despite what many people believe, a dark-red colouring of the gums is not a positive sign in dental aesthetics. The true colour of dental health is rather a bright-pink colouring!
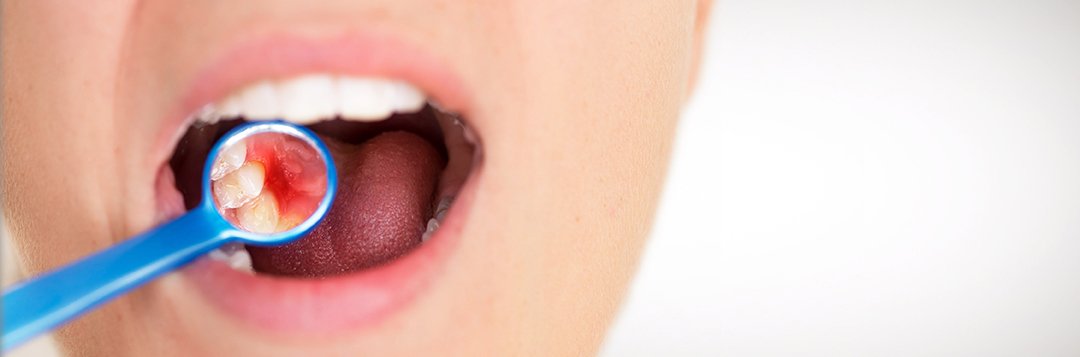
The structure of the gums and the process of inflammation
At the precise point where tooth and gum meet is where the junctional epithelium can be found. When good oral hygiene and a balanced diet are maintained, this epithelium layer (a specialised layer of the gum tissue) provides protection against inflammation of the peridontium (teeth-supporting structures), which can even last an entire lifetime. The initial stage of bleeding of the gums occurs when there is insufficient oral hygiene. As such, bleeding of the gums in any given affected area is a good indicator for, and is generally caused by, a bacterial infection on the tooth. In this case, experts refer to a case of acute gingivitis, which can still be remedied by following oral hygiene instructions and taking the appropriate steps. If steps are not taken to stop the advancing of the disease, the gums subsequently become so loose that it becomes easy for bacteria to invade deeper and deeper into the gingival crevice. For the patient, however, it becomes more and more difficult to remove these bacteria reaching deeper and deeper into the gingival crevices. The bacteria are highly specialised when it comes to taking hold in these niches and carrying out their function. If this process occurs in many different areas, the disease is them termed “generalised acute gingivitis”.
If this inflammation persists over a long period of time, then it is referred to as chronic gingivitis, either acute or generalised.
If this process continues still further, then the inflammation spreads to the peridontium. This is when experts will refer to “paradontosis”. The peridontium is made up of the gums (bordering the teeth), the fibres that hold the teeth into place, and the jawbone itself.
If paradontosis disease cannot be treated with a paradontosis treatment, then in the worst case, this may lead to tooth loss. These cases are often referred to as “severe chronic periodontal disease”. A common factor to all diseases in this regard is that bacterial deposits, tartar, and plaques are not removed through sufficient cleaning of the teeth and act as the cause of a subsequent gingivitis.
Causes and symptoms
In addition to bleeding of the gums, a symptom and initial sign is that your gums feel sensitive when brushing. Bacteria are not the only possible cause, but they do play a major role.
Other causes may also include mechanical irritation which occurs due to damage caused to gums due to brushing with toothbrushes that are too hard, or using toothpicks, or through overly aggressive flossing. This is where bacteria can invade the resulting wound and cause inflammation. Changing to softer toothbrushes and using interdental brushes generally help in this case.
Further causes for increased risk of suffering from gingivitis include type II diabetes, pregnancy, day-to-day stress, and of course, smoking.
On top of that, gingivitis can itself lead to an increased risk of suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
In the case of smokers, nicotine impedes the helpful blood supply which would help to prevent disease. During pregnancy, hormonal changes cause gums to become weaker due to certain enzymes which cause tissues to expand. This results in an elevated risk of suffering from gingivitis and periodontal disease (paradontosis ).
Type-II diabetics suffer from an increased permeability of the blood-vessel walls, which results in an increased risk for both gingivitis and periodontal disease (in specialist jargon: periodontitis).

“Recognising inflammation of the gums is eminently important in order to protect against subsequent changes which cannot be rectified”. As the dentists at the Dr. Hager Dental Practice, we particularly focus our attention on cases of gingivitis, and explain the most common causes of bleeding of the gums. This allows us to guarantee our patients’ long-term dental health.“
Benjamin Hager, Dentist at the Dr. Hager Dental Practice
Stopping gingivitis: the Dr. Hager approach
There are simple rules for oral hygiene which can stop gingivitis. Regular tooth brushing, combined with cleaning the spaces between teeth using dental floss or small interdental brushes and a professional clean 2-to-4 times per year will help to cure cases of gingivitis and stop periodontal disease in its tracks.
The Dr. Hager dentists have developed a safe and simple treatment approach to achieve exactly that, ensuring patients’ safety, trust and treatment success.
If bleeding of the gums occurs, indicating inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), patients at the Dr. Hager Dental Practice are put on a closely monitored treatment plan. The treatment begins with professional tooth cleaning and clearly defining the basic oral hygiene measures that need to be taken at home. In most cases, these measures will cause any bleeding of the gums to stop. In cases where periodontal disease has taken hold (also known as “Periodontal disease (paradontosis)”), we also have a specifically developed, and scientifically-backed treatment approach for stopping the periodontal disease in a short space of time. Needless to say, all treatments are carried out using a local anaesthetic.
Frequently asked questions
How long does an acute inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) last?
Gingivitis will persist until it has been cured. This can be achieved by following simple rules on oral hygiene measures to be taken at home. The difficulty here is for patients to identify this type of inflammation. For this reason, regular tooth cleaning appointments are recommended. With just these simple measures, you can go a long way in ensuring life-long dental health.
Gum inflammation: what can I do about it?
Gum inflammation comes about due to untreated plaque build-up, vitamin C deficiency, harmful bacteria, and poor oral hygiene.
Do I need to see a dentist if I have gum inflammation?
The longer inflammation of the gums goes untreated, the greater the risk of periodontal disease occurring. For this reason, it is clearly important in the case of gum diseases for any inadequate oral hygiene to be remedied: dental hygienists at the Dr. Hager Dental Practice will give you the right advice and information and provide treatment to bring your gums back into good health.
How do dentists treat inflammation of the gums?
The dentists at the Dr. Hager Dental Practice know gum diseases inside out. They will carry out a thorough inspection of the gums (as well as the rest of the mouth) during an appointment with you, allowing for the possible onset of disease to be prevented. Where required, treatment will be given for any inflammation of the gums. In addition to this, a periodontal screening index is determined in order to proceed with a treatment for periodontal disease if needed.
What is gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums in the mouth. Indicative signs include bleeding of the gums, and without treatment it may lead to periodontal disease: an inflammation of the surrounding tissues that support the teeth (the periodontium).
When does inflammation of the gums go away?
As soon as patients start to take the correct steps for oral hygiene, inflammation improves. The human immune system also helps here. The steps that you need to take from that point on can be explained to you by the dental hygienists at the Dr. Hager Dental Practice. Arrange an appointment online with us today!